
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- COVID-19
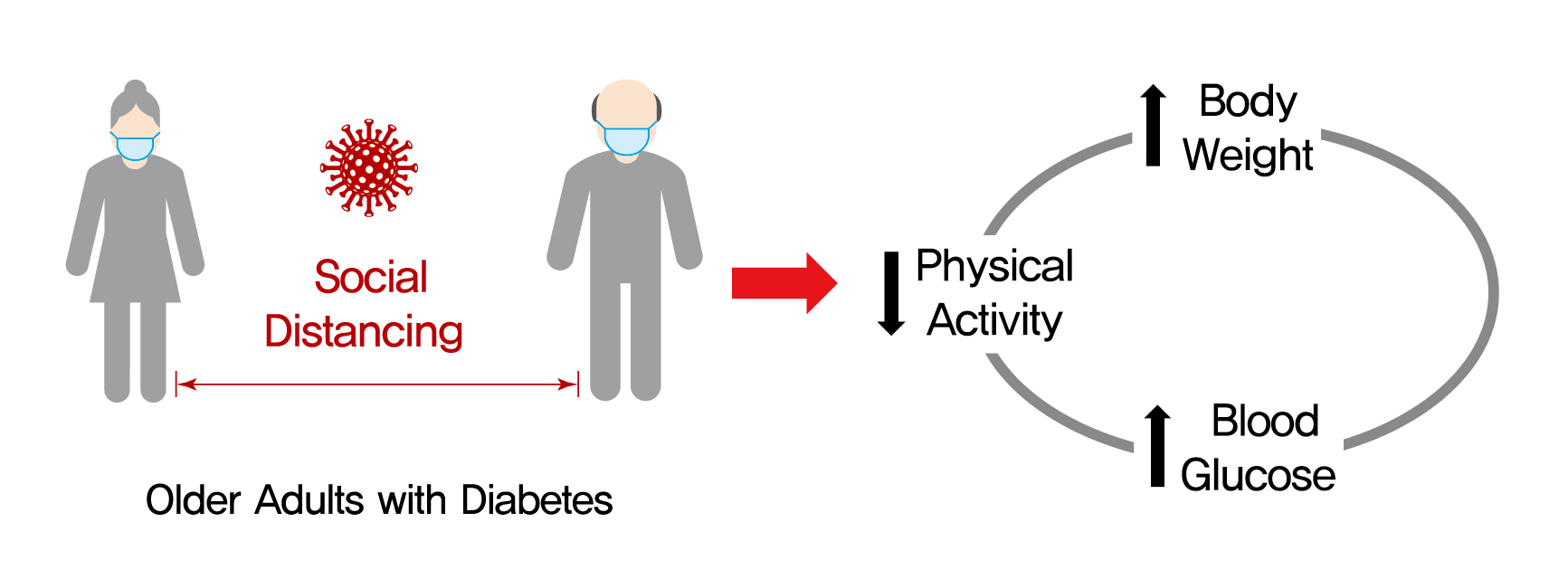
- Effects of Social Distancing on Diabetes Management in Older Adults during COVID-19 Pandemic
- Soo Myoung Shin, Tae Jung Oh, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):765-772. Published online August 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0096
- 5,967 View
- 191 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
On March 22, 2020, intense social distancing (SD) was implemented in Korea to prevent the spread of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19). This study examined the impact of SD on diabetes control in older adults with diabetes.
Methods
Adults aged 60 to 90 years with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were physically and mentally independent were recruited. Participants who had complete blood chemistry data from April to July 2019 (pre-SD era) and April to July 2020 (SD era) were enrolled. Data were obtained about physical activity, nutrition, sarcopenia, and psychological and mental health from questionnaires in April to July 2020. Calf circumference was measured.
Results
In total, 246 people (100 men, 146 women; mean age, 73.8±5.7 years) participated in this study. The levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c, 7.4%±1.0% vs. 7.1%±0.8%, P<0.001), fasting glucose (142.2±16.7 mg/dL vs. 132.0±27.7 mg/dL, P<0.001), and body weight (62.6±9.4 kg vs. 61.8±10.1 kg, P<0.01) were higher in the SD era than in the pre-SD era. Total physical activity was lower in the SD era (2,584.6±2,624.1 MET-min/week–1 vs. 1,987.3±2,295.0 MET-min/week–1, P<0.001). A larger increase in HbA1c level was associated with increased body weight and decreased physical activity.
Conclusion
SD had negative effects on diabetes management in older adults with diabetes. Fasting glucose and HbA1c levels and body weight increased during the SD era. Participants with reduced physical activity gained more weight and had higher blood glucose levels. Given that the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, health professionals and diabetes educators should monitor changes in lifestyle factors in older adults with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Preliminary efficacy of a technology-based physical activity intervention for older Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic
Soonhyung Kwon, Oejin Shin, Rosalba Hernandez
Educational Gerontology.2024; 50(1): 27. CrossRef - Obesity and weight change during the COVID‐19 pandemic in children and adults: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Laura N. Anderson, Yulika Yoshida‐Montezuma, Nora Dewart, Ezza Jalil, Jayati Khattar, Vanessa De Rubeis, Sarah Carsley, Lauren E. Griffith, Lawrence Mbuagbaw
Obesity Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in lifestyle-related behaviour during the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan: a questionnaire survey for examinees who underwent an annual health check-up
Miyako Kishimoto, Kayo Masuko, Sumie Yamamoto, Retsu Fujita, Shoko Nakamura, Masato Odawara, Mikio Zeniya
Journal of International Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycaemic monitoring and control among high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes in Australian general practice during COVID-19
Kirrilee Jane Barlow, Paul P Fahey, Evan Atlantis
Family Medicine and Community Health.2023; 11(3): e002271. CrossRef - Social isolation, loneliness and subsequent risk of major adverse cardiovascular events among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yannis Yan Liang, Yilin Chen, Hongliang Feng, Huachen Xue, Yu Nie, Qi-Yong H Ai, Jiacheng Ma, Lulu Yang, Jihui Zhang, Sizhi Ai
General Psychiatry.2023; 36(6): e101153. CrossRef - Stress, Depression, and Unhealthy Behavior Changes among Patients with Diabetes during COVID-19 in Korea
Hae Ran Kim, Jeong-Soon Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(2): 303. CrossRef - Reply to comment on “Unexpected decline in glycated hemoglobin level after emergency COVID‐19 measures in three robust older Japanese women with prediabetes/mild type 2 diabetes”
Tazuo Okuno, Osamu Iritani, Kumie Kodera, Daisuke Hama, Asami Kane, Kozue Morigaki, Toshio Terai, Norie Maeno, Shigeto Morimoto
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2022; 22(7): 541. CrossRef - Anxiety, Distress and Stress among Patients with Diabetes during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Rubén A. García-Lara, José L. Gómez-Urquiza, María José Membrive-Jiménez, Almudena Velando-Soriano, Monserrat E. Granados-Bolivar, José L. Romero-Béjar, Nora Suleiman-Martos
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(9): 1412. CrossRef - Prevalence of Depression and Related Factors among Patients with Chronic Disease during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Rubén A. García-Lara, Nora Suleiman-Martos, María J. Membrive-Jiménez, Victoria García-Morales, Miguel Quesada-Caballero, Isabel M. Guisado-Requena, José L. Gómez-Urquiza
Diagnostics.2022; 12(12): 3094. CrossRef
- Preliminary efficacy of a technology-based physical activity intervention for older Korean adults during the COVID-19 pandemic

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





